David M. Albala, MD, presented “Live-Primary Cell Phenotypic Biomarkers and Prostate Cancer Prognosis” during the 29th Annual International Prostate Cancer Update on January 24, 2019 in Beaver Creek, Colorado.
How to cite: Albala, David M. “Live-Primary Cell Phenotypic Biomarkers and Prostate Cancer Prognosis” January 24, 2019. Accessed Apr 2024. https://dev.grandroundsinurology.com/live-primary-cell-phenotypic-biomarkers-and-prostate-cancer-prognosis/
Live-Primary Cell Phenotypic Biomarkers and Prostate Cancer Prognosis
David M. Albala, MD, emphasizes the need for improved prostate cancer diagnostics to allow for better risk-stratification and guidance of personalized treatment. He then reviews findings from an analytical validation study of live-primary cell phenotypic biomarker-based diagnostic assay with the potential to address this need.
Abstract:
Due to inconsistencies in existing molecular, genomic, and pathophysiologic markers for patient risk-stratification, effective prostate cancer diagnostics and treatment remains a challenge in clinical practice. Therefore, the development of a diagnostic platform that differentiates cancer patients who have clinically significant disease from those who have a low-risk of progression is an important area of interest.
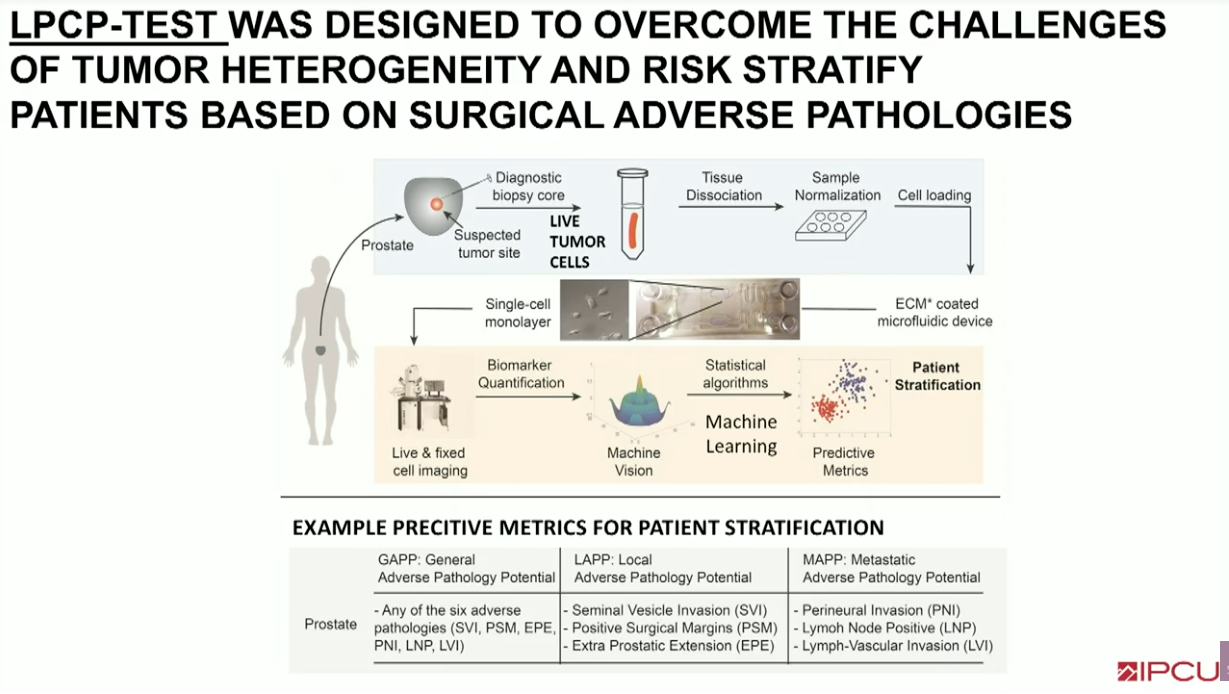
To address this issue, a diagnostic platform was tested that combines a scalable microfluidic device, enabling an automated live cell assay. This assay measures phenotypic biomarkers (as defined here as functional biophysical and molecular biomarkers) via objective machine vision algorithms to evaluate both local invasive and metastatic potential of prostate cancer.
An analytical validation study was performed on fresh prostate cancer samples (n=238) obtained at the time of radical prostatectomy (RP). The diagnostic platform enables: 1) growth of patient cells ex vivo on extracellular matrix formulations supporting adhesion/survival for 72 hours post biopsy; 2) high-throughput imaging of multiple phenotypic biomarkers such as morphology, cytoskeleton dynamics, and protein subcellular localization & modification states; and 3) objective quantification of biomarkers via machine vision analysis. The study imaged patient samples over a three-hour period, capturing live-cell biophysical biomarkers. After three hours, cells were fixed and stained for molecular biomarkers. Machine vision technology was then utilized to analyze phenotypic biomarkers to yield specific metrics that correlated with RP specimen pathologic findings.
Predictive scores for the risk stratification of 238 prostate cancer patients, with values for area under the curve in receiver-operating-characteristic curves surpassing 80%, support the validation of the assay and its potential clinical applicability for the prognosis and risk-stratification of prostate cancer patients.
About the International Prostate Cancer Update
The International Prostate Cancer Update (IPCU) is an annual, multi-day CME conference focused on prostate cancer treatment updates. The conference’s faculty consists of international experts, and the event caters to urologists, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and other healthcare professionals. Topics encompass prostate cancer management, from diagnosis to treating advanced and metastatic disease. Dr. Albala presented this lecture during the 29th IPCU in 2019. Please visit this page in order to learn more about future IPCU meetings.