A simple way to assign or allocate the fixed costs is to base it on things such as direct labor hours, machine hours, or pounds of direct material. Accountants realize that this is simplistic; they know that overhead costs are caused by many different factors. Nonetheless, we will assign the fixed manufacturing overhead costs to the aprons by using the direct labor hours.
Variable Overhead Spending Variance
The standard overhead cost is usually expressed as the sum of its component parts, fixed and variable costs per unit. Note that at different levels of production, total fixed costs are the same, so the standard fixed cost per unit will change for each production level. However, the variable standard cost per unit is the same per unit for each level of production, but the total variable costs will change. Because fixed overhead costs are not typically driven byactivity, Jerry’s cannot attribute any part of this variance to theefficient (or inefficient) use of labor.
AccountingTools
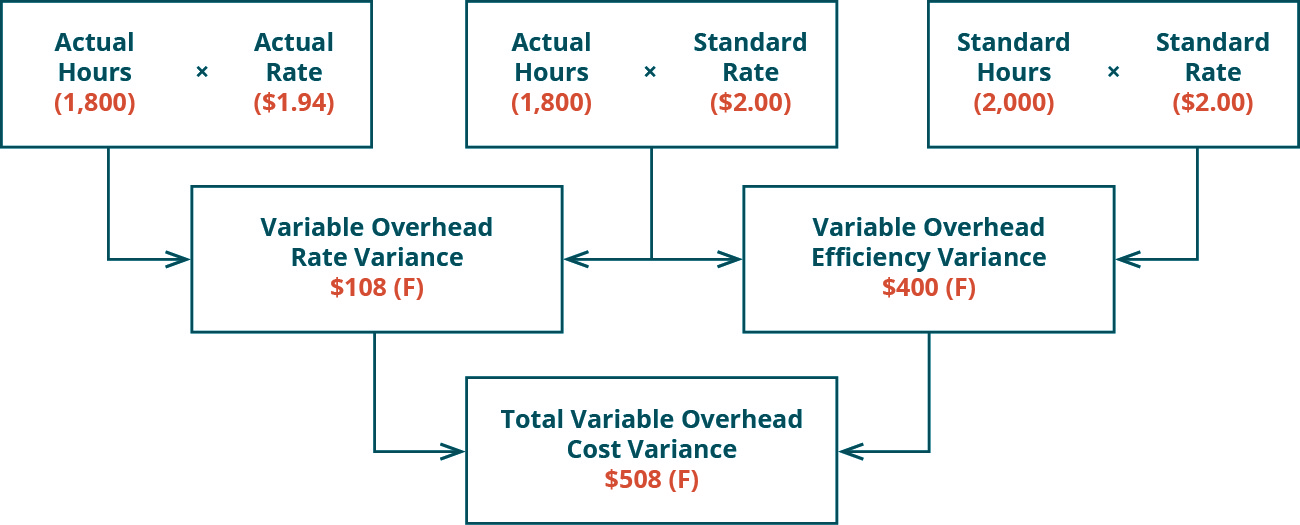
This is due to the actual production volume that it has produced in August is 50 units lower than the budgeted one. However, as the name suggested, it is the fixed overhead volume variance that is more about the production volume. Likewise, we can also determine whether the fixed overhead volume variance is favorable or unfavorable by simply comparing the actual production claiming a parent as a dependent volume to the budgeted production volume. The total variable overhead cost variance is also found by combining the variable overhead rate variance and the variable overhead efficiency variance. By showing the total variable overhead cost variance as the sum of the two components, management can better analyze the two variances and enhance decision-making.
What is Fixed Overhead Spending Variance? Definition, Formula, Explanation, And Analysis
Another variable overhead variance to consider is the variable overhead efficiency variance. The fixed overhead volume variance is also one of the main standard costing variances, and is the difference between the standard fixed overhead allocated to production and the budgeted fixed overhead. A favorable fixed overhead spending variance arises when the actual fixed overheads incurred by the company are lower than the budgeted fixed overheads. This result of $950 of unfavorable fixed overhead volume variance can be used together with the fixed overhead budget variance to determine the total fixed overhead variance. As a result, the company has an unfavorable fixed overhead variance of $950 in August.
9: Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Variance Analysis
Although the fixed manufacturing overhead costs present themselves as large monthly or annual expenses, they are part of each product’s cost. It is important to start by noting that fixed overhead in themaster budget is the same as fixed overhead in the flexible budgetbecause, by definition, fixed costs do not change with changes inunits produced. Thus budgeted fixed overhead costs of $140,280shown in Figure 10.12 will remain the same even though Jerry’sactually produced 210,000 units instead of the master budgetexpectation of 200,400 units. The total variable overhead cost variance is also found by combining the variable overhead rate variance and the variable overhead efficiency variance. An unfavorable or adverse fixed overhead spending variance would arise when the actual fixed overheads exceed the budgeted fixed overheads. Standard fixed overhead rate can be calculated with the formula of budgeted fixed overhead cost dividing by the budgeted production volume.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
A favorable variance may occur due to economies of scale, bulk discounts for materials, cheaper supplies, efficient cost controls, or errors in budgetary planning. Since the expenditure is considered to be under the control of management, the overhead budget variance is referred to as a controllable variance. They do not vary as the output varies unless a specific point is crossed and it becomes stepped costs instead of fixed costs. After the reasons have been highlighted the company takes measures to deal with any material variances throughout the year to minimize costs.
He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. If the balances are considered insignificant in relation to the size of the business, then they can simply be transferred to the cost of goods sold account. As shown in the example above, Tahkila Industrial had a favorable variance for the year ended 2019 since they had to pay $80,000 less than expected. Motors PLC is a manufacturing company specializing in the production of automobiles.
- This system, which treats fixed manufacturing costs as a product cost, is required for external financial statements.
- The fixed factory overhead variance represents the difference between the actual fixed overhead and the applied fixed overhead.
- This could be for many reasons, and the production supervisor would need to determine where the variable cost difference is occurring to make production changes.
- If the outcome is favorable (a negative outcome occurs in the calculation), this means the company was more efficient than what it had anticipated for variable overhead.
- If the amount applied to the good output is greater than the budgeted amount of fixed manufacturing overhead, the fixed manufacturing overhead volume variance is favorable.
- Variable overhead spending variance is the difference between actual variable overhead cost, which is based on the costs of indirect materials involved in manufacturing, and the budgeted costs called the standard variable overhead costs.
Therefore, these variances reflect the difference between the standard cost of overheads allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual overhead cost incurred. This could be for many reasons, and the production supervisor would need to determine where the variable cost difference is occurring to better understand the variable overhead efficiency reduction. Estimate the total number of standard direct labor hours that are needed to manufacture your products during 2023. We indicated above that the fixed manufacturing overhead costs are the rents of $700 per month, or $8,400 for the year 2023.
The fixed overhead volume variance is the difference between the amount of fixed overhead actually applied to produced goods based on production volume, and the amount that was budgeted to be applied to produced goods. For example, a company budgets for the allocation of $25,000 of fixed overhead costs to produced goods at the rate of $50 per unit produced, with the expectation that 500 units will be produced. However, the actual number of units produced is 600, so a total of $30,000 of fixed overhead costs are allocated.
The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Mohit Khera, MD, MBA, MPH, is the Professor of Urology and Director of the Laboratory for Andrology Research at the McNair Medical Institute at Baylor College of Medicine. He is also the Medical Director of the Executive Health Program at Baylor. Dr. Khera earned his undergraduate degree at Vanderbilt University. He subsequently earned his Masters in Business Administration and his Masters in Public Health from Boston University. He received his MD from The University of Texas Medical School at San Antonio and completed his residency training in the Scott Department of Urology at Baylor College of Medicine. He then went on to complete a one-year Fellowship in Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery with Dr. Larry I. Lipshultz, also at Baylor.
Dr. Khera specializes in male infertility, male and female sexual dysfunction, and declining testosterone levels in aging men. Dr. Khera’s research focuses on the efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in treating Peyronie’s disease, as well as genetic and epigenetic studies on post-finasteride syndrome patients and testosterone replacement therapy.
Dr. Khera is a widely published writer. He has co-authored numerous book chapters, including those for the acclaimed Campbell-Walsh Urology textbook, for Clinical Gynecology, and for the fourth edition of Infertility in the Male. He also co-edited the third edition of the popular book Urology and the Primary Care Practitioner. In 2014, he published his second book Recoupling: A Couple’s 4 Step Guide to Greater Intimacy and Better Sex. Dr. Khera has published over 90 articles in scientific journals and has given numerous lectures throughout the world on testosterone replacement therapy and sexual dysfunction. He is a member of the Sexual Medicine Society of North America, the American Urological Association, and the American Medical Association, among others.




