Nelson N. Stone, MD, presented “Long-Term Erectile Dysfunction and Urinary Morbidity Following Brachytherapy” during the 23rd Annual Southwest Prostate Cancer Update on April 15, 2018 in Scottsdale, Arizona
How to cite: Stone, Nelson N. “Long-Term Erectile Dysfunction and Urinary Morbidity Following Brachytherapy” April 15, 2018. Accessed [date today]. https://dev.grandroundsinurology.com/long-term-erectile-dysfunction-and-urinary-morbidity-following-brachytherapy/
Long-Term Erectile Dysfunction and Urinary Morbidity Following Brachytherapy – Summary:
Nelson N. Stone, MD, discusses changes in urinary symptoms and erectile function, as measured by the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPPS), at 10 and 15 years following prostate brachytherapy. Subsequently, he advises clinicians on best practices in seed implantation and long-term management to optimize cancer control and minimize adverse symptoms.
Long-Term Data Following Prostate Brachytherapy
10 Year Data
In 2012, Dr. Stone and a research group published a study in The Journal of Urology measuring urinary symptoms at 10 years after permanent prostate seed brachytherapy. The 15 year version will come out later this summer.
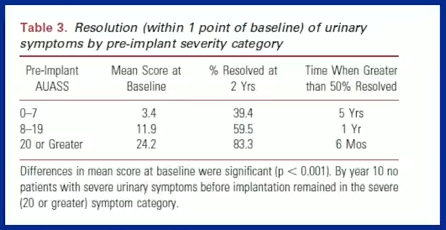
The 10 year version reported data from about 2,000 patients who completed 11,491 IPSS symptom sheets. Mean urinary scores changed from a baseline of 7.4 to 7.8 at the ten year mark.
Additionally, the study measured patient responses according to whether they initially had minimal, moderate, or severe symptoms. This study found that implanted patients with initially severe symptoms improved over a 10 year period. Those patients also resolved symptoms, on average, six months after implantation, while those who had initially minimal symptoms, on average saw, resolution at five years.
There were no substantial differences between patients treated with or without hormonal therapy.
15 Year Data
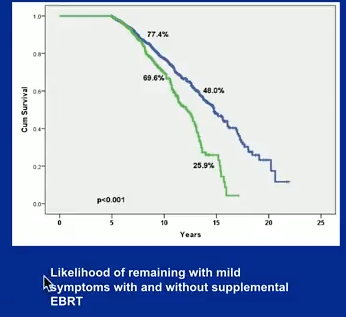
Dr. Stone hopes to publish the 15 year version of this study later this summer. While 10 year reporting showed minimal changes in symptoms, only 40% of patients remained with an IPPS score between 0-7 at 15 years.
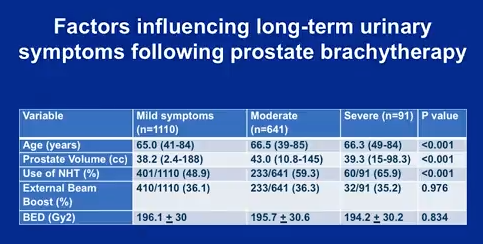
Most notably, these results support that the addition of external beam boost and higher radiation doses exacerbate the likelihood of patients progressing to a higher symptom group.
Best Practices to Avoid Worsening Urinary Symptoms
Prostate brachytherapy, while linked to adverse effects on urinary function, is extremely effective for local cancer control. Therefore, Dr. Stone addresses challenges in brachytherapy practice and describes methods to minimize these adverse symptoms.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Nelson N. Stone, MD, is Professor of Urology, Radiation Oncology, and Oncological Sciences at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and at the Derald H. Ruttenberg Cancer Center at Mount Sinai. He also serves as CEO of 3D Biopsy, LLC.
Dr. Stone earned his medical degree from the University of Maryland in 1979. He completed a Residency in General Surgery in 1981 at the University of Maryland, followed by a Residency in Urology at the University of Maryland. He then completed a Fellowship in Urologic Oncology at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center and a Research Fellowship in Biochemical Endocrinology at Rockefeller University in 1986. He was Chief of Urology at Elmhurst Hospital from 1989-1996.
Dr. Stone has founded several medical companies and serves on the editorial board of many scientific journals. He is a member of many professional societies, including the Prostate Conditions Education Council, the Society for Minimally Invasive Therapy, the New York State Urological Society, the American Association of Clinical Urologists, and the American Urologic Association. Dr. Stone has participated in approximately 25 research studies on prostate cancer and has authored more than 400 articles, abstracts, and book chapters, primarily on prostate cancer. He invented the real-time technique for prostate seed implantation in 1990 and has trained more than 5,000 physicians worldwide on prostate brachytherapy through his company ProSeed. His company, 3DBiopsy, Inc., is developing variable length biopsy devices, mapping software, and an integrated pathology system.